Although this report might not be useful to everyone, the method of altering the data within the report might be of use.
The report essentially provides a list of all systems that have certain software installed, and presents the CPU and Operating System information for each.
The software titles to include in the report are retrieved from a separate database which can be edited by end-users with Orchestrator runbooks.
The recipients of the report wanted to retrieve a list of systems based on a predefined software list (Microsoft SQL Server, Symantec NetBackup Client etc etc). I was keen not to hard code this list of software into the report query because A: there were nearly 100 software titles to report on, which would look pretty messy in the query, and B: Software titles needed to be added and removed easily.
I created a couple of data tables on a separate database (CM_Runtime) to hold the lists of software they wanted to report on, one for Windows (dbo.reportsoftware) and the other for Linux (dbo.reportapplications).
The query to retrieve the system lists based on the contents of dbo.reportsoftware and dbo.reportapplications is below.
select distinct
SMS_R_System.Name0 AS [Server],
SMS_R_System.Resource_Domain_OR_Workgr0 AS Domain,
___System_INSTALLED_SOFTWARE0.ARPDisplayName00 AS [Application Name],
SMS_G_System_PROCESSOR.NumberOfCores00 AS [Number of Cores],
SMS_G_System_COMPUTER_SYSTEM.NumberOfProcessors00 AS [Number of Processors],
SMS_G_System_PROCESSOR.NumberOfLogicalProcessors00 AS [Number of Logical CPUs],
SMS_G_System_OPERATING_SYSTEM.Caption00 AS [Operating System]
from
vSMS_R_System AS SMS_R_System
INNER JOIN INSTALLED_SOFTWARE_DATA AS ___System_INSTALLED_SOFTWARE0 ON ___System_INSTALLED_SOFTWARE0.MachineID = SMS_R_System.ItemKey
INNER JOIN Processor_DATA AS SMS_G_System_PROCESSOR ON SMS_G_System_PROCESSOR.MachineID = SMS_R_System.ItemKey
INNER JOIN Computer_System_DATA AS SMS_G_System_COMPUTER_SYSTEM ON SMS_G_System_COMPUTER_SYSTEM.MachineID = SMS_R_System.ItemKey
INNER JOIN Operating_System_DATA AS SMS_G_System_OPERATING_SYSTEM ON SMS_G_System_OPERATING_SYSTEM.MachineID = SMS_R_System.ItemKey
INNER JOIN _RES_COLL_SMSDM003 AS SMS_CM_RES_COLL_SMSDM003 ON SMS_CM_RES_COLL_SMSDM003.MachineID = SMS_R_System.ItemKey
where
___System_INSTALLED_SOFTWARE0.ARPDisplayName00 in
( SELECT InstalledSoftware
FROM CM_RunTime.dbo.reportsoftware )
UNION
select distinct
SMS_R_System.Name0 AS [Server],
SMS_R_System.Resource_Domain_OR_Workgr0 AS Domain,
__System_ADD_REMOVE_PROGRAMS0.DisplayName00 AS [Application Name],
SMS_G_System_PROCESSOR.NumberOfCores00 AS [Number of Cores],
SMS_G_System_COMPUTER_SYSTEM.NumberOfProcessors00 AS [Number of Processors],
SMS_G_System_PROCESSOR.NumberOfLogicalProcessors00 AS [Number of Logical CPUs],
SMS_G_System_OPERATING_SYSTEM.Caption00 AS [Operating System]
from
vSMS_R_System AS SMS_R_System
INNER JOIN Add_Remove_Programs_DATA AS __System_ADD_REMOVE_PROGRAMS0 ON __System_ADD_REMOVE_PROGRAMS0.MachineID = SMS_R_System.ItemKey
INNER JOIN Processor_DATA AS SMS_G_System_PROCESSOR ON SMS_G_System_PROCESSOR.MachineID = SMS_R_System.ItemKey
INNER JOIN Computer_System_DATA AS SMS_G_System_COMPUTER_SYSTEM ON SMS_G_System_COMPUTER_SYSTEM.MachineID = SMS_R_System.ItemKey
INNER JOIN Operating_System_DATA AS SMS_G_System_OPERATING_SYSTEM ON SMS_G_System_OPERATING_SYSTEM.MachineID = SMS_R_System.ItemKey
where __System_ADD_REMOVE_PROGRAMS0.DisplayName00
in
( SELECT InstalledApplications
FROM CM_RunTime.dbo.reportapplications )
Adding and Removing Software in Report
I made an initial bulk import of software to the data tables using PowerShell, but for ongoing management I've configured Orchestrator to remove or add rows to the tables using a couple of runbooks:
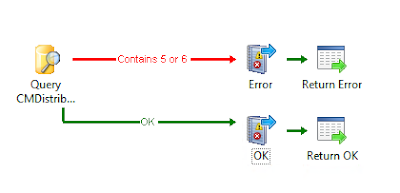
(Remove Software title)
(Add Software title)
Each runbook initialize data properties are as follows:

To add a software title the 'Write to Database' activity is used.
To remove a software title the 'Query Database' activity is used.
A list of the current software titles held in the data tables is sent each time the tables are edited using a PowerShell script to retrieve the data and create a CSV, and then it's emailed.
# Set script parameters from runbook data bus and Orchestrator global variables
# Define any inputs here and then add to the $argsArray and script block parameters below
$ReportPath = "D:\SCORCH Data\SoftwareReports\softwarereport-$(Get-Date -Format yyyyMMddHHmmss).csv"
$Username = "#SQLUSER#"
$Password = "#PASSWORD#"
$Database = "CM_Runtime"
$SQLServer = "#SQLSERVERNAME#"
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------
## Initialize result and trace variables
# $ResultStatus provides basic success/failed indicator
# $ErrorMessage captures any error text generated by script
# $Trace is used to record a running log of actions
$ResultStatus = ""
$ErrorMessage = ""
$Trace = (Get-Date).ToString() + "`t" + "Runbook activity script started" + " `r`n"
# Create argument array for passing data bus inputs to the external script session
$argsArray = @()
$argsArray += $ReportPath
$argsArray += $Username
$argsArray += $Password
$argsArray += $Database
$argsArray += $SQLServer
# Establish an external session (to localhost) to ensure 64bit PowerShell runtime using the latest version of PowerShell installed on the runbook server
# Use this session to perform all work to ensure latest PowerShell features and behavior available
$Session = New-PSSession -ComputerName localhost
# Invoke-Command used to start the script in the external session. Variables returned by script are then stored in the $ReturnArray variable
$ReturnArray = Invoke-Command -Session $Session -Argumentlist $argsArray -ScriptBlock {
# Define a parameter to accept each data bus input value. Recommend matching names of parameters and data bus input variables above
Param(
[ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
[string]$ReportPath,
[ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
[string]$Username,
[ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
[string]$Password,
[ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
[string]$Database,
[ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
[string]$SQLServer
)
# Define function to add entry to trace log variable
function AppendLog ([string]$Message)
{
$script:CurrentAction = $Message
$script:TraceLog += ((Get-Date).ToString() + "`t" + $Message + " `r`n")
}
# Set external session trace and status variables to defaults
$ResultStatus = ""
$ErrorMessage = ""
$script:CurrentAction = ""
$script:TraceLog = ""
try
{
# Add startup details to trace log
AppendLog "Script now executing in external PowerShell version [$($PSVersionTable.PSVersion.ToString())] session in a [$([IntPtr]::Size * 8)] bit process"
AppendLog "Running as user [$([Environment]::UserDomainName)\$([Environment]::UserName)] on host [$($env:COMPUTERNAME)]"
AppendLog "Parameter values received:ReportPath=[$ReportPath] Database=[$Database] SQLServer=[$SQLServer]"
# The actual work the script does goes here
AppendLog "SQL Query to retrieve"
$Array = @(Invoke-SQLCmd -query "SELECT InstalledApplications AS [Software] FROM dbo.reportapplications UNION SELECT InstalledSoftware AS [Software] FROM dbo.reportsoftware" -Server $SQLServer -Username $Username -Password $Password -Database $Database)
AppendLog "Writing to CSV File"
$Array | ConvertTo-Csv -NoTypeInformation |
% {$_.Replace('"','')} |
Out-File $ReportPath -Encoding ascii
# Validate results and set return status
AppendLog "Finished work, determining result"
$EverythingWorked = $true
if($EverythingWorked -eq $true)
{
$ResultStatus = "Success"
}
else
{
$ResultStatus = "Failed"
}
}
catch
{
# Catch any errors thrown above here, setting the result status and recording the error message to return to the activity for data bus publishing
$ResultStatus = "Failed"
$ErrorMessage = $error[0].Exception.Message
AppendLog "Exception caught during action [$script:CurrentAction]: $ErrorMessage"
}
finally
{
# Always do whatever is in the finally block. In this case, adding some additional detail about the outcome to the trace log for return
if($ErrorMessage.Length -gt 0)
{
AppendLog "Exiting external session with result [$ResultStatus] and error message [$ErrorMessage]"
}
else
{
AppendLog "Exiting external session with result [$ResultStatus]"
}
}
# Return an array of the results. Additional variables like "myCustomVariable" can be returned by adding them onto the array
$resultArray = @()
$resultArray += $ResultStatus
$resultArray += $ErrorMessage
$resultArray += $script:TraceLog
$resultArray += $myCustomVariable
return $resultArray
}#End Invoke-Command
# Get the values returned from script session for publishing to data bus
$ResultStatus = $ReturnArray[0]
$ErrorMessage = $ReturnArray[1]
$Trace += $ReturnArray[2]
$MyCustomVariable = $ReturnArray[3]
# Record end of activity script process
$Trace += (Get-Date).ToString() + "`t" + "Script finished" + " `r`n"
# Close the external session
Remove-PSSession $Session